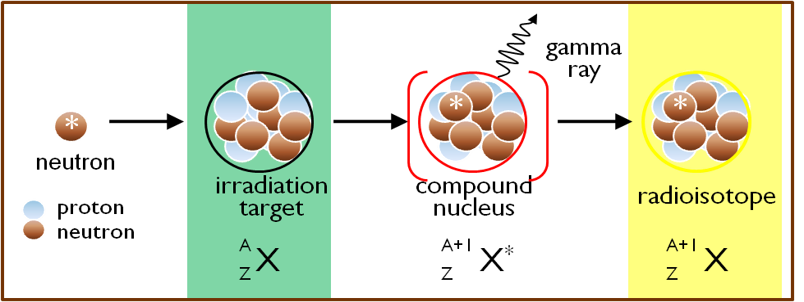
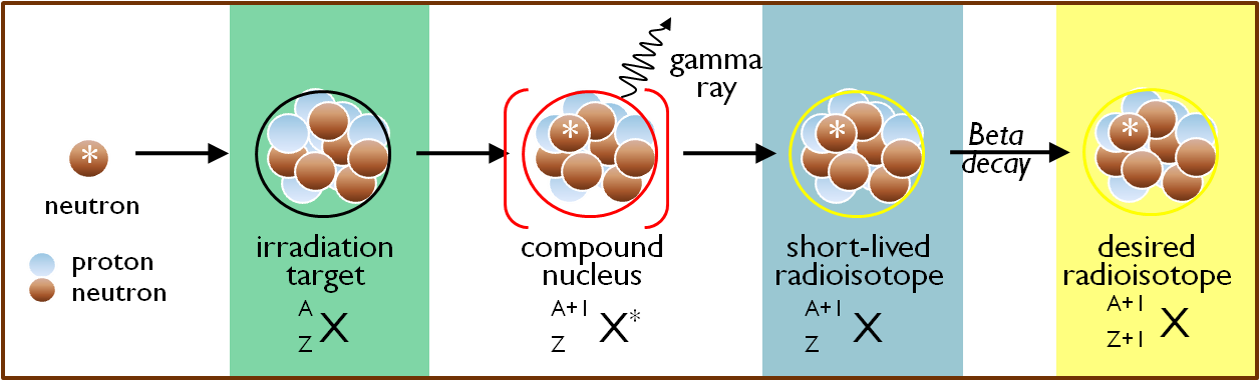
A variation on this method is to generate a short-lived radioisotope that undergoes radioactive decay to yield the longer-lived radioisotope of interest. This strategy is used for the production of high specific activity iodine-125, which is a beta- decay product of xenon-125 formed when xenon-124 captures a neutron. A wide variety of radioisotopes can be produced at MNR by neutron irradiation of appropriate target materials.
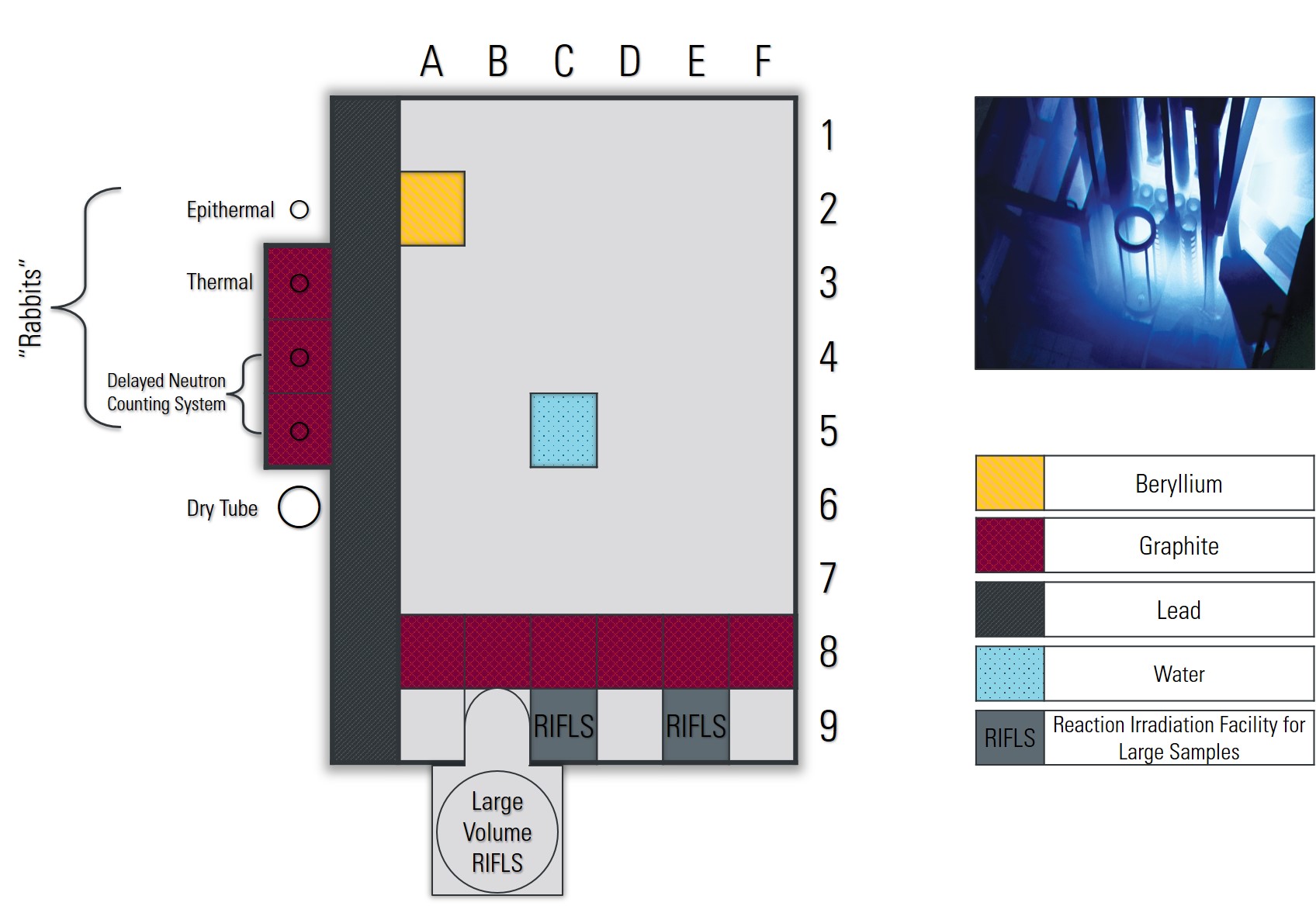
A wide variety of isotopes can be made at the McMaster Nuclear Reactor using by placing samples in-core or using the various “Rabbit” systems. Several well characterized sites with varying neutron fluxes are available for use, with graphite or beryllium reflected sites, or lead-shielded sites. Depending on the nature of the sample, cadmium lining is also available for fast neutron irradiations. To learn more about isotopes previously made in the reactor, check out our core irradiations page, or for specific questions contact reactor@mcmaster.ca .